Wood Gasification
The aim of wood gasification is to generate through a thermodynamic conversion of dried wood a fuel gas, from which electricity and heat can be produced in a second step.
Already in the 1930s and 1940s, methods for wood gasification were developed to move vehicles and trains. Advancements were dismissed because of strong soot and tar generation.
In search of sustainable and economically viable energy sources the method has been adopted to the present needs. Today it is possible to produce a combustible gas and generate mechanical energy from it.
The Method
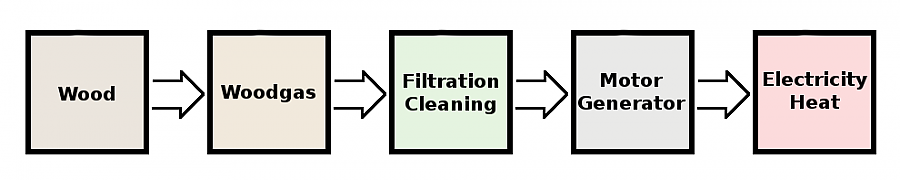
By heating up wood to 1000 degrees and reducing the air supply, a combustible gas – the wood gas – is extracted. The gas is then filtered and purified from substances such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen and methane in order to receive a climate neutral fuel.
This climate neutral fuel is particularly environmental friendly, because the process releases only as much carbon dioxide as the tree removed from the atmosphere.
Finally, electricity and heat is generated from the purified gas in an efficient way.
Another advantage of wood gasification is that there is no recovery system with a higher efficiency of electricity production.
The Plant
The operation of a wood gasification system is fully automatic. All control-related parameters are constantly monitored, recorded and balanced whilst shown on the visualization display.
An integrated Telenot system provides information on all current operating conditions of the plant and corrective interventions can be made through a standard internet connection at any time.
We offer wood gasification plant systems in collaboration in Alto Adige and the rest of Italy with our partner URBAS, a leader in Europe in the technology of wood gasification.